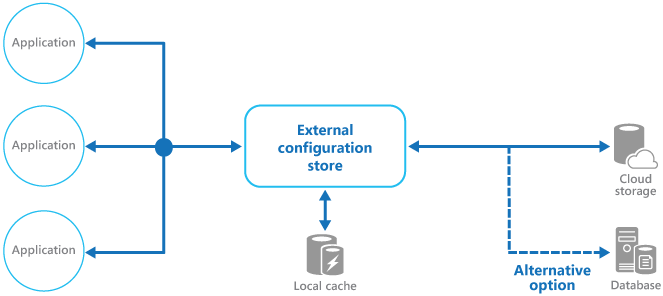
外部配置存储模式
将应用程序部署包中的配置信息放在集中位置。这可以提供更容易管理和控制配置数据以及跨应用程序和应用程序实例共享配置数据的机会。
背景和问题
大多数应用程序运行时环境,包括在文件中保存的配置信息,与应用程序一起部署。在某些情况下,可以通过编辑这些文件,以便在部署后更改应用程序行为。但是,配置的更改需要重新部署应用程序,通常会导致无法接受的停机时间和其它管理开销。 本地配置文件也将配置限制在单个应用程序中,但有时跨多个应用程序共享配置设置将非常有用。比如数据库连接字符串,UI主题信息或相关应用程序集使用的队列和存储的URL。 在应用程序的多个运行实例中管理本地配置的更改具有挑战性,特别是托管在云平台的场景中。部署更新时可能导致实例使用不同配置设置。 此外,应用程序和组件的更新可能需要更改配置schema。许多配置系统不支持不同版本的配置信息。
解决方案
将配置信息存在的外部存储,并且提供快速有效地读取和更新配置设置的接口。外部存储的类型取决于应用程序的托管和运行时环境。在云托管场景中,通常是基于云的存储服务,也可以是托管数据库或其它系统。 为配置信息选择的后台存储应具有提供一致且易于使用的访问接口。应该以正确类型和结构化的格式暴露信息。实现还可能需要授权用户访问以保护配置数据,并且足够灵活,以允许存储多个版本的配置(例如开发,预生产或生产环境,包括多个发布版本)。
许多内置的配置系统在应用程序启动时读取数据,并将数据缓存在内存中,快速访问并最大限度地减少对应用程序性能的影响。根据所使用的备份存储的类型和该存储的延迟,在外部配置存储中实现缓存机制可能会有所帮助。更多相关信息请参阅缓存指南。下图概述了具有可使用本地缓存的外部配置存储模式。
问题和注意事项
在决定如何实现此模式时,请考虑以下几点:
选择一个提供性能可接受,可用性高,鲁棒的备份存储,并可作为应用程序维护和管理过程的一部分进行备份。在云托管应用中,使用云存储机制通常是满足这些要求的好选择。
设计后备存储的schema,以允许其容纳信息类型的灵活性。确保它提供所有配置要求,例如类型化数据,设置集合,多个版本的设置以及应用程序所需的任何其它功能。该schema应该易于扩展,以便在需求更改时支持其它设置。
考虑备份存储的物理功能,这与存储配置信息的方式以及对性能的影响有关。例如,存储包含配置信息的XML文档将需要配置接口或应用程序来解析文档,以便读取单独的设置。这将使更新设置更加复杂,但是缓存设置可以帮助抵消较慢的读取性能。
考虑配置接口如何允许控制配置设置的范围和继承。例如,可能需要在组织,应用程序和机器级别范围内配置设置。可能需要支持授权对不同作用域的访问的控制,并阻止或允许各个应用程序覆盖设置。
考虑如何保护配置数据,以便仅允许合法的用户和应用程序访问。这可能是配置存储接口的一个功能,但是还有必要确保备份存储中的数据在没有适当权限的情况下无法直接访问。确保读取和写入配置数据所需的权限之间的严格分离。还要考虑是否需要加密部分或全部配置设置,以及如何在配置存储接口中实现。
确保配置接口按照要求的格式(如键入值,集合,键/值对或属性包)公开配置数据。
考虑当设置出错时,或者备份存储中不存在时,配置存储接口的行为。可以返回默认设置并记录错误。同时还要考虑诸如区分配置设置键或名称大小写,二进制数据的存储和处理以及处理null或空值的方式等方面。
考虑如何保护配置数据,以便仅访问适当的用户和应用程序。这可能是配置存储界面的一个功能,但是还有必要确保后台存储中的数据无法在没有适当权限的情况下直接访问。确保读取和写入配置数据所需的权限之间的严格分隔。还要考虑是否需要加密部分或全部配置设置,以及如何在配置存储界面中实现。
在运行时更改应用程序行为的集中存储配置至关重要,应使用与部署应用程序代码相同的机制进行部署,更新和管理。例如,影响多个应用程序的更改必须使用完整的测试和分段部署方法,以确保更改适用于使用此配置的所有应用程序。如果管理员编辑更新一个应用程序的设置,则可能会对使用相同设置的其它应用程序造成不利影响。
如果应用程序缓存配置信息,则应用程序需要在配置更改时收到警报。可以在缓存的配置数据上实现一个过期策略,以便定期自动刷新此信息,并获取(并采取行动)的任何更改。
何时使用该模式
该模式适用于以下场景:
- 在多个应用程序和应用程序实例之间共享的配置设置,或者必须在多个应用程序和应用程序实例之间执行标准配置。
- 不支持所有必需配置设置的标准配置系统,例如存储图像或复杂数据类型。
- 作为应用程序某些设置的补充存储,可能允许应用程序覆盖部分或全部集中存储的设置。
- 作为一种简化多个应用程序管理的方法,并且可选择的通过记录对配置存储的一些或所有类型的访问来监视配置设置的使用。
案例
在Microsoft Azure托管应用程序中,一般使用Azure Storage外部存储配置信息。具备弹性同时提供高性能,有三个副本,出现故障时会自动切换以提供高可用性。Azure Table存储提供了键/值存储,可以为值的使用灵活的schema。Azure Blob存储提供了一个分层的基于容器的存储,可以在单独命名的blob中保存任何类型的数据。
下面的例子显示如何通过Blob存储实现配置存储的存储和公开配置信息。BlobSettingsStore类用于保存配置信息的Blob存储,并实现以下代码中展示的ISettingsStore接口。
ExternalConfigurationStore解决方案的ExternalConfigurationStore.Cloud项目的代码可以在github上找到。
该代码在ExternalConfigurationStore解决方案中的ExternalConfigurationStore.Cloud项目中提供,可从GitHub获得。
public interface ISettingsStore
{
Task<string> GetVersionAsync();
Task<Dictionary<string, string>> FindAllAsync();
}
该接口定义了用于检索和更新配置存储中保存的配置设置的方法,并包括可用于检测是否最近修改了任何配置设置的版本号。 BlobSettingsStore类使用blob的ETag属性来实现版本控制。每次写入blob时,ETag属性都会自动更新。
根据设计,这个简单的解决方案将所有配置设置暴露为字符串而不是类型值。
ExternalConfigurationManager类围绕BlobSettingsStore对象提供了一个包装器。应用程序可以使用它来存储和检索配置信息。它使用Microsoft Reactive Extensions库实现IObservable接口暴露对配置所做的任何更改。如果通过调用SetAppSetting方法修改设置,则会出发Changed事件,并通知事件的所有订阅者。
请注意,所有设置也会缓存在ExternalConfigurationManager类中的Dictionary对象中,以便快速访问。用于检索配置设置的GetSetting方法从缓存读取数据。如果缓存中没有找到设置,它将从BlobSettingsStore对象中检索。
GetSettings方法调用CheckForConfigurationChanges来检测blob存储中的配置信息是否已更改。它通过检查版本号并将其与ExternalConfigurationManager对象持有的当前版本号进行比较。如果发生一个或多个更改,则会出发Changed事件,并刷新Dictionary对象中缓存的配置设置。这是Cache-Aside模式的一个应用。
以下代码示例显示Changed事件,GetSettings方法和CheckForConfigurationChanges方法如何实现的:
public class ExternalConfigurationManager : IDisposable
{
// An abstraction of the configuration store.
private readonly ISettingsStore settings;
private readonly ISubject<KeyValuePair<string, string>> changed;
...
private readonly ReaderWriterLockSlim settingsCacheLock = new ReaderWriterLockSlim();
private readonly SemaphoreSlim syncCacheSemaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(1);
...
private Dictionary<string, string> settingsCache;
private string currentVersion;
...
public ExternalConfigurationManager(ISettingsStore settings, ...)
{
this.settings = settings;
...
}
...
public IObservable<KeyValuePair<string, string>> Changed => this.changed.AsObservable();
...
public string GetAppSetting(string key)
{
...
// Try to get the value from the settings cache.
// If there's a cache miss, get the setting from the settings store and refresh the settings cache.
string value;
try
{
this.settingsCacheLock.EnterReadLock();
this.settingsCache.TryGetValue(key, out value);
}
finally
{
this.settingsCacheLock.ExitReadLock();
}
return value;
}
...
private void CheckForConfigurationChanges()
{
try
{
// It is assumed that updates are infrequent.
// To avoid race conditions in refreshing the cache, synchronize access to the in-memory cache.
await this.syncCacheSemaphore.WaitAsync();
var latestVersion = await this.settings.GetVersionAsync();
// If the versions are the same, nothing has changed in the configuration.
if (this.currentVersion == latestVersion) return;
// Get the latest settings from the settings store and publish changes.
var latestSettings = await this.settings.FindAllAsync();
// Refresh the settings cache.
try
{
this.settingsCacheLock.EnterWriteLock();
if (this.settingsCache != null)
{
//Notify settings changed
latestSettings.Except(this.settingsCache).ToList().ForEach(kv => this.changed.OnNext(kv));
}
this.settingsCache = latestSettings;
}
finally
{
this.settingsCacheLock.ExitWriteLock();
}
// Update the current version.
this.currentVersion = latestVersion;
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
this.changed.OnError(ex);
}
finally
{
this.syncCacheSemaphore.Release();
}
}
}
ExternalConfigurationManager类还提供了一个名为Environment的属性。它支持在不同环境(如分段和生产)中运行的应用程序的不同配置。
ExternalConfigurationManager对象也可以定期查询BlobSettingsStore对象的任何更改。在下面的代码中,StartMonitor方法会以一定时间间隔调用CheckForConfigurationChanges,检测任何更改并引发更改事件,如前所述。
public class ExternalConfigurationManager : IDisposable
{
...
private readonly ISubject<KeyValuePair<string, string>> changed;
private Dictionary<string, string> settingsCache;
private readonly CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
private Task monitoringTask;
private readonly TimeSpan interval;
private readonly SemaphoreSlim timerSemaphore = new SemaphoreSlim(1);
...
public ExternalConfigurationManager(string environment) : this(new BlobSettingsStore(environment), TimeSpan.FromSeconds(15), environment)
{
}
public ExternalConfigurationManager(ISettingsStore settings, TimeSpan interval, string environment)
{
this.settings = settings;
this.interval = interval;
this.CheckForConfigurationChangesAsync().Wait();
this.changed = new Subject<KeyValuePair<string, string>>();
this.Environment = environment;
}
...
/// <summary>
/// Check to see if the current instance is monitoring for changes
/// </summary>
public bool IsMonitoring => this.monitoringTask != null && !this.monitoringTask.IsCompleted;
/// <summary>
/// Start the background monitoring for configuration changes in the central store
/// </summary>
public void StartMonitor()
{
if (this.IsMonitoring)
return;
try
{
this.timerSemaphore.Wait();
// Check again to make sure we are not already running.
if (this.IsMonitoring)
return;
// Start running our task loop.
this.monitoringTask = ConfigChangeMonitor();
}
finally
{
this.timerSemaphore.Release();
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Loop that monitors for configuration changes
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public async Task ConfigChangeMonitor()
{
while (!cts.Token.IsCancellationRequested)
{
await this.CheckForConfigurationChangesAsync();
await Task.Delay(this.interval, cts.Token);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Stop monitoring for configuration changes
/// </summary>
public void StopMonitor()
{
try
{
this.timerSemaphore.Wait();
// Signal the task to stop.
this.cts.Cancel();
// Wait for the loop to stop.
this.monitoringTask.Wait();
this.monitoringTask = null;
}
finally
{
this.timerSemaphore.Release();
}
}
public void Dispose()
{
this.cts.Cancel();
}
...
}
ExternalConfigurationManager类由以下所示的ExternalConfiguration类实例化为单例实例。
public static class ExternalConfiguration
{
private static readonly Lazy<ExternalConfigurationManager> configuredInstance = new Lazy<ExternalConfigurationManager>(
() =>
{
var environment = CloudConfigurationManager.GetSetting("environment");
return new ExternalConfigurationManager(environment);
});
public static ExternalConfigurationManager Instance => configuredInstance.Value;
}
以下代码取自ExternalConfigurationStore.Cloud项目中的WorkerRole类。它显示了应用程序如何使用ExternalConfiguration类来读取设置。
public override void Run()
{
// Start monitoring configuration changes.
ExternalConfiguration.Instance.StartMonitor();
// Get a setting.
var setting = ExternalConfiguration.Instance.GetAppSetting("setting1");
Trace.TraceInformation("Worker Role: Get setting1, value: " + setting);
this.completeEvent.WaitOne();
}
下面的代码也来自WorkerRole类,显示应用程序如何订阅配置事件。
public override bool OnStart()
{
...
// Subscribe to the event.
ExternalConfiguration.Instance.Changed.Subscribe(
m => Trace.TraceInformation("Configuration has changed. Key:{0} Value:{1}",
m.Key, m.Value),
ex => Trace.TraceError("Error detected: " + ex.Message));
...
}
相关模式和指南
- GitHub上有本模式使用的简单例子。